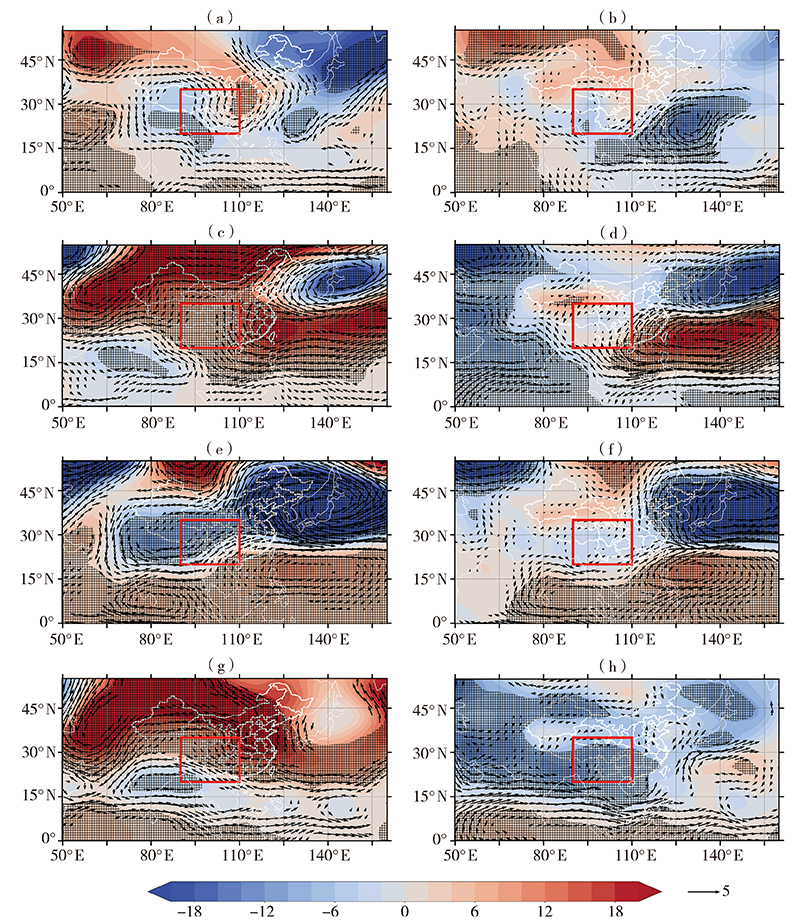
青藏高原夏季风和北半球夏季季节内振荡对中国西南地区雨季旱涝的影响及协同作用
Individual and joint influence of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon and boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation on drought and flood in rainy season of southwestern China
(网格填色区域和箭头均通过α=0.05的显著性检验,红色方框包围区域为中国西南地区。下同)
(a、b)B1-23-AQ,(c、d)B1-56-AQ,(e、f)B2-34-AQ,(g、h)B2-67-AQ
(The color grid areas and arrows pass the significance test at 0.05 level, and the area enclosed by the red box is the southwestern China. the same as below)
(a, b) B1-23-AQ, (c, d) B1-56-AQ, (e, f) B2-34-AQ, (g, h) B2-67-AQ