天山南坡暖季暴雨过程的水汽来源及输送特征
Water vapor source and transport characteristics of rainstorm processes in warm season on southern slope of the Tianshan Mountains
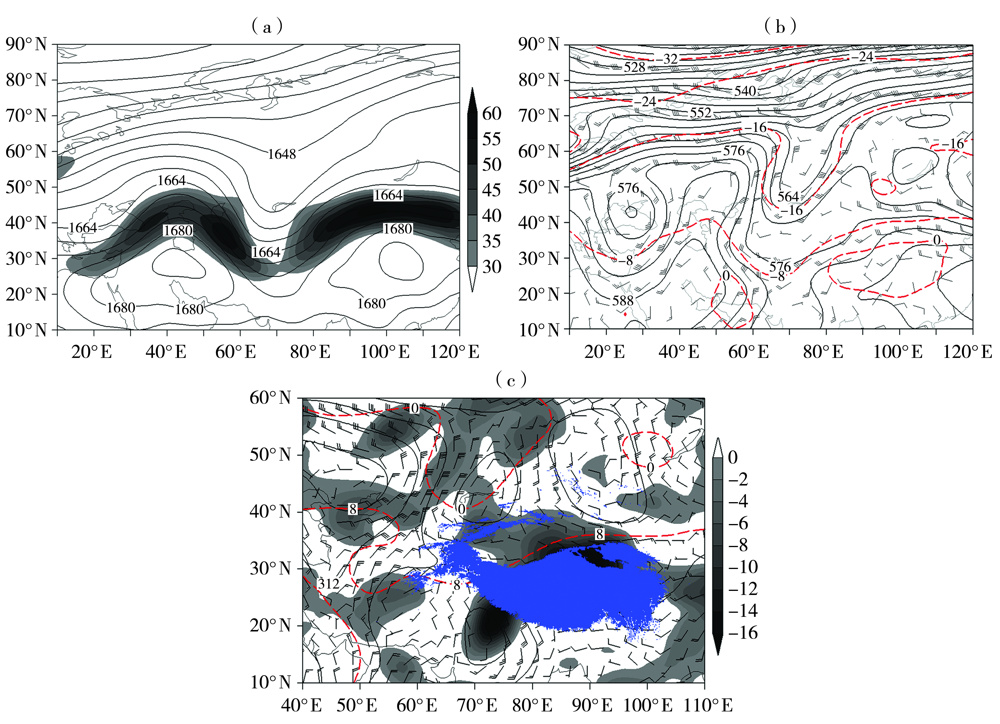
(a)100 hPa位势高度场(等值线,单位:dagpm)和200 hPa高空急流(阴影,单位:m·s-1), (b)500 hPa位势高度场(黑色实等值线,单位:dagpm)、风场(风羽,单位:m·s-1)及温度场(红色虚等值线,单位:℃), (c)700 hPa位势高度场(黑色实等值线,单位:dagpm)、风场(风羽,单位:m·s-1)、 温度场(红色虚等值线,单位:℃)及水汽通量散度(阴影,单位:10-6 g·hPa-1·cm-2·s-1) (蓝色区域为3000 m以上高度的青藏高原)
(a) 100 hPa geopotential height field (isolines, Unit: dagpm) and 200 hPa upper-level jet stream (shadow, Unit: m·s-1), (b) 500 hPa geopotential height field (black solid isolines, Unit: dagpm), wind field (barbs, Unit: m·s-1) and temperature field (red dotted isolines, Unit: ℃), (c) 700 hPa geopotential height field (black solid isolines, Unit: dagpm), wind field (barbs, Unit: m·s-1), temperature field (red dotted isolines, Unit: ℃) and water vapor flux divergence (shadows, Unit: 10-6 g·hPa-1·cm-2·s-1) (the blue area for the Tibet Plateau with elevation more than 3000 m)